Rights of NRN in Nepal: A Complete Guide
Rights of NRNs in Nepal: Key Insights
Rights of NRNs in Nepal: Key Insights
NRNs Services & Consulting is the First Platform dedicated to providing Legal, Financial and other Services to Non-Resident Nepali with 20 Years of Global Expertise and experience of serving countless NRN’s. This article has covered the fundamental details about NRNs, their rights, benefits, legal obligations and rights and more.
What does NRN stand for?
NRN stands for Non-Resident Nepali, and the term, according to the Non-resident Nepali Act, 2064, denotes two major categories:
1. Foreign Citizen of Nepalese Origin, also known as FCRA, are individuals with Foreign Citizenship but with Nepalese Heritage.
2. Nepali Citizen Residing Abroad, also known as NCRA, are Nepali Citizens in Foreign Countries through Nepalese Passport.

Who are Foreign Citizen of Nepalese Origin?
A “foreign citizen of Nepalese origin” is someone who, or whose father, mother, grandfather, or grandmother, was once a citizen of Nepal and later became a citizen of another country, excluding SAARC member countries.
Who are Nepali Citizen Residing Abroad?
A “Nepali citizen residing abroad” is a Nepali citizen who has lived in a foreign country for at least two years for work, business, or employment but not in a SAARC member country, on a diplomatic mission, or as a student.
Who qualifies as an NRN?
To qualify as an NRN, the individual must have Valid Citizenship of another country with Nepali Heritage. However, Nepali Citizens residing abroad for more than two years also qualify as an NRN.
It is important to understand if the individual is eligible as a Non-Resident Nepali to exercise the rights conferred upon such Individuals.
Are NRNs only Nepali?
The Term NRN, which stands for Non-Resident Nepali, is used to denote individuals residing in a foreign country with a Nepalese Heritage.
Individuals of other heritage, such as Indian and Bangladeshi heritage, don’t qualify as non-resident Nepali.
It is legally required for an individual to have a reasonable connection with Nepal, either parents or grandparents to have been Nepali Citizens to be considered as such.
Can NRNs hold dual citizenship?
After the Latest Amendment of the Nepal Citizenship Regulations, NRN’s can legally acquire dual citizenship of their country of residence along with the Citizenship of Nepal. The Citizenship of Nepal conferred to such individuals, has limited rights and benefits, generally being limited to Social, Economic and Cultural.
NRN Services & Consulting provides comprehensive services to individuals seeking Legal, Property, Financial and Tax Services in Nepal. The Firm has 20 years of Global Expertise in serving Clients across 12 Countries.
What is the NRNA Association?
NRNA which stands for Non-Resident Nepali Organization is an umbrella organization for all Nepali Citizens or individuals of Nepalese Origin residing abroad. The Organization itself was established to unite the Nepali Diaspora for the Social and Economic Development of Nepal and Nepali Heritage.
The Organization was conceived in Russia in 2002 A.D. after which Nepali Community Leaders throughout the globe met in London in 2003 to form a Coordination Committee. The Organization was further materialized with the Non-Resident Nepali Conference in October 2003. The Association is actively involved in assisting NRN’s and Nepalese Citizens.
How many NRNs are there worldwide?
Officially, the Non-Resident Nepali Association has 1,06,912 members registered. However, the count of the Nepali Diaspora is global. However, the estimation of Nepali Individuals, either by citizenship or Heritage, is nearly 30,00,000 and above.
What are the Rights of NRN in Nepal?
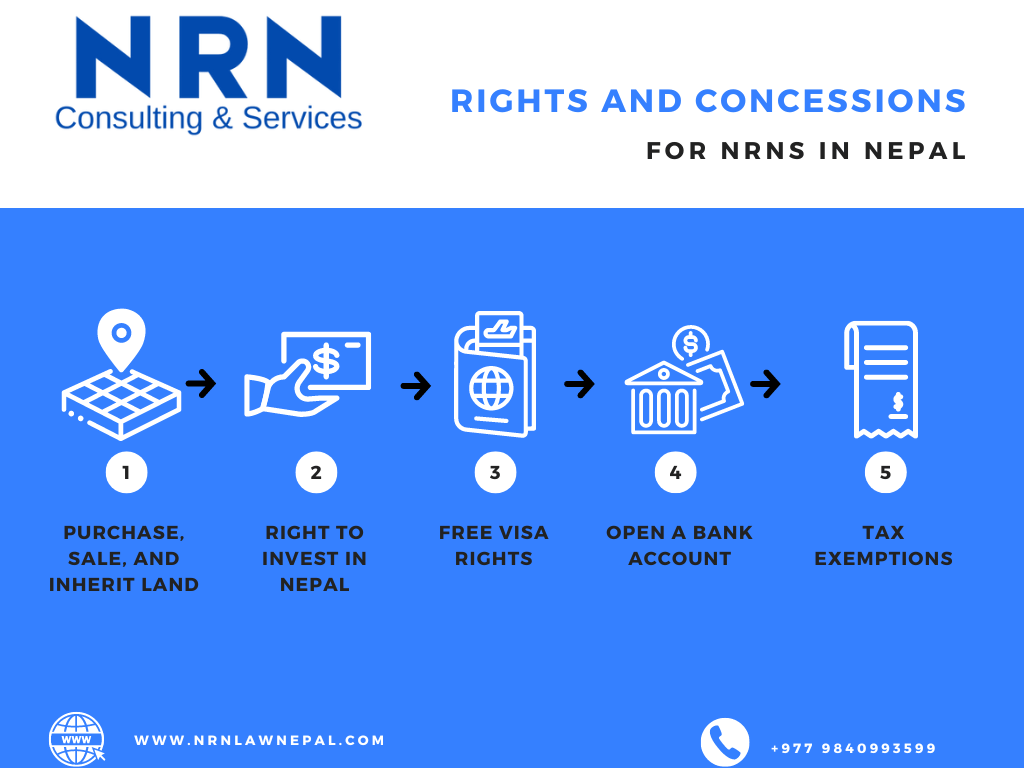
The Benefits conferred to Non-Resident Nepali, with either the ID Card or the Citizenship, are as follows:
1. Rights to Purchase Property
Individuals have the right to purchase property in Nepal, including land, houses, and other real estate. However, the right is limited to a Maximum of 2 Ropani in the Kathmandu Valley and so forth. The Right allows such individuals to maintain a Physical and Financial Presence in Nepal and provide economic opportunities.
2. Right to Invest in Nepal
Individuals can also invest in various sectors of the Nepali Economy such as starting businesses, investing in industries and participating in Joint Ventures. It can also attract investment from the Global Nepali Community and create Job opportunities within the country.
3. VISA rights (Extended)
Individuals also benefit from extended and exclusive VISA rights to ease their travel to and from Nepal by obtaining long-term Visas, which increases the flexibility for individuals who frequently travel between Nepal and other Countries.
4. Additional Social, Cultural and Economic Rights.
NRN Citizenship also grants several Social, Cultural and Economic Rights to individuals with the Citizenship, allowing them to maintain a strong connection to their heritage and community.
NRN Services and Consulting also provides Hourly Consultations to individuals interested in conducting business, buying property and conducting Real Estate Transactions in Nepal.
Do NRNs pay taxes in Nepal?
Nepalese tax law differentiates between resident and non-resident taxpayers. Resident taxpayers are required to declare their global income and pay taxes on it in Nepal. This means that if a person is considered a resident for tax purposes, they must report all their earnings, regardless of where in the world they are generated, and pay taxes based on Nepalese tax rates.
For non-resident taxpayers, the rules are different. Non-residents, including NRNs, only need to declare and pay taxes on the income they earn within Nepal. This provision simplifies the tax obligations for NRNs, as they are not required to report income earned outside of Nepal to the Nepalese tax authorities.
NRNs, as non-resident taxpayers, have to pay taxes on their earnings in Nepal. The Eligible income from investments, property rentals, businesses, or any other sources within the country. For instance, if an NRN owns property in Nepal and earns rental income, they must report this income and pay the applicable taxes in Nepal.
Can NRNs invest in Nepal?
Yes, Non-Resident Nepali can conduct investment in Nepal but the investment must be conducted through the Procedure established by Foreign Investment and Technology Transfer Act, 2019. Despite holding relevant card or citizenship, the individual cannot conducted investment through other routes.
However, to conduct the investment in any capacity, individuals desiring such investment must have cleared all tax obligations and obtained necessary permits for investing in Nepal.
Are NRNs allowed to buy property in Nepal?
Non-Resident Nepali (Foreign Citizen of Nepali Origin) are allowed to purchase any land in any one of the region to reside within Nepal for for the sake of their Family.

Land Ownership Limits in Nepal
Location Maximum Land Area Allowed
Kathmandu Valley 2 Ropani
Municipalities in Terai 8 Kattha
Other Municipalities 4 Ropani
Village Development Committees in Terai 1 Bigaha
Other Areas 10 Ropani
Individuals have specific limits on the amount of land they can own in different parts of Nepal. In the Kathmandu Valley, up to 2 Ropani of land can be owned. In the Municipalities of Terai District, up to 8 Kattha of land can be owned. For other Municipalities outside the Kathmandu Valley and the Terai Region, up to 4 Ropani of Land can be owned. For Rural municipalities in Terai Districts, up to 1 Bigha of land can be owned. Moreover, for other areas, up to 10 Ropani of land can be owned.
How do NRNs contribute to Nepal’s economy?
Individuals can contribute to the Nepalese Economy by purchasing Real Estate, Property, or other investments. They can also conduct Investments in the sectors allowed by the Foreign Investment and Technology Transfer Act of 2019 and get relevant approval from the Department of Industry.
NRNs can also conduct charity, programs, donations, and assistance with people in need to contribute to Nepal’s economy.
Can NRNs participate in Nepali elections?
Non-resident Nepalis, usually foreign Citizens of Nepali Origin, cannot participate in Nepali Elections or cast votes in any manner.
The Latest Citizenship provided to such individuals has allowed for Social, Economic and Cultural Rights.
Do NRNs have a special status in Nepal?
Yes, they have a special status in Nepal as they usually require an ID Card or Citizenship to exercise the rights, duties and obligations laid forth.
Can NRNs start businesses in Nepal?
Yes, NRNs can start businesses in Nepal by conducting Foreign Direct Investment in the relevant sector. NRN Services & Consulting advises non-resident Nepali investors on the procedure, approvals, and additional details for starting such businesses in Nepal.
What rights do NRNs have in Nepal?

The Rights of Non-Resident Nepali individuals after obtaining ID Card in Nepal are:
Free Visa to Enter and Stay in Nepal
NRNs holding citizenship of countries outside the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) are entitled to free visas for entering and staying in Nepal. This allows for simpler Travel Arrangements and active participation without the burden of Visa Fees.
Right to Open a Bank Account in Convertible Foreign Currency:
NRNs can open bank accounts in Nepal that hold convertible foreign currency. It facilitates transactions and investments within Nepal and keep funds accessible in an internationally recognized Currency.
Eligibility to Make Investments in Convertible Foreign Currency:
NRNs are eligible to make investments in Nepal using convertible foreign currency. It allows the Injection of Foreign Capital into the Nepalese Economy.
Provision to Repatriate Proceeds of Investment:
NRNs can repatriate the proceeds from their investments in Nepal in the same convertible foreign currency used for the initial investment.
Purchase and Sale of Land
NRNs can purchase and sell land in Nepal within the limits specified in the Non-Resident Nepali Association (NRNA) bylaws. These regulations set maximum land ownership areas based on location.
Inheritance of Ancestral Property
NRNs have the right to inherit ancestral property in Nepal and maintain ownership of such property.
Tax Exemption on Initial Capital of Investment
The initial capital invested by NRNs in Nepal is exempt from taxes.
Tax Exemption on Remittances to Close Relatives:
NRNs are entitled to a tax exemption on remittances up to NPR 15 lakhs sent to close relatives in Nepal within one fiscal year for personal expenses.
Tax Exemption for Specific Projects:
Funds remitted by NRNs through formal banking channels for social, political, cultural, religious, charity, sports, and disaster relief projects are exempt from taxes.
Rights to Establish Industry and Business:
NRNs have the right to establish industries and businesses in Nepal, enjoying the same investment facilities as foreign investors.
Are NRNs eligible for Nepali government jobs?
Individuals who have forfeited Nepali Citizenship and have become Foreign Citizens aren’t eligible for Nepali Government Jobs or in any public Office unless specified as such. However, individuals can reacquire their citizenship certificate from Nepal.
Conclusion
NRN Services & Consulting is a leading platform offering legal, financial, and other essential services tailored for Non-Resident Nepalis (NRNs). The Firm has 20 years of Global Expertise and serves numerous NRNs. To qualify as an NRN, individuals must have valid foreign citizenship with Nepalese heritage. Nepali citizens living abroad for more than two years also qualify. NRN Services & Consulting provides comprehensive support for legal, property, financial, and tax matters in Nepal.
FAQs
What is NRN Services & Consulting?
NRN Services & Consulting is the First Platform offering legal, financial, and other services to Non-Resident Nepalis (NRNs) with 20 Years of Combined Global Expertise.
What does NRN stand for?
NRN Stands for Non-Resident Nepali and includes Foreign Citizens of Nepali Origin (FCRA) or Nepali Citizens Residing Abroad (NCRA).
Who are FCNO and NCRA?
Individuals with foreign citizenship but Nepalese heritage, excluding SAARC countries, qualify as Foreign Citizens of Nepalese Origin. Nepali citizens living abroad for at least two years for work or business, excluding SAARC countries, qualify.
Can NRNs hold dual citizenship?
Yes, NRNs can legally hold dual citizenship of their resident country and Nepal, with limited rights.
Can NRNs invest in Nepal?
Yes, NRNs can invest in Nepal following the Foreign Investment and Technology Transfer Act, 2019.
What rights do NRN carry in Nepal?
Non-Resident Nepali can have free visa to enter and stay in Nepal, Right to open a bank account, eligibility to make investment in foreign currency, repatriate proceeds of investment, purchase and sale of land, inheritance of ancestral property and more.
Can NRNs start Businesses in Nepal?

NRNs can start businesses in Nepal through Foreign Direct Investment.
