NRN Court Case in Nepal: A How-to Guide 2026
NRN Services & Consulting is renowned for its leading Lawyers in Nepal including Senior Advocates and seasoned Litigators with Nationally acclaimed Practice. The Firm can provide the best legal representation to Non-Resident Nepali or find the right lawyer who can. This Article covers the detailed guide to handling NRN Court Case in Nepal.
Can NRNs file Court Case in Nepal?

Yes, Non-Resident Nepalis (NRNs) have the right to file lawsuits in Nepal. However, there are certain procedures and requirements they must adhere to. NRNs can file lawsuits related to various matters such as property disputes, business conflicts, or personal injury claims.
NRN Services & Consulting provides expert legal consultation to understand your legal position and suggest the best method to approach the case at hand.
What is the process for NRN Court Case in Nepal?
The court process for NRNs in Nepal follows similar procedures as for Nepali citizens. NRNs can initiate legal proceedings by filing a case in the appropriate court based on the nature and jurisdiction of the dispute.
The court process typically involves submitting a written complaint or petition, followed by hearings where evidence is presented and arguments are made. NRNs may need to engage legal representation.

How to hire a litigation lawyer?
To hire a litigation lawyer in Nepal, NRNs should consider several factors such as the lawyer’s expertise, experience, reputation, and fees. It’s essential to research and gather recommendations from trusted sources or legal directories. NRNs can schedule consultations with potential lawyers to discuss their case and evaluate their suitability.
During the consultation, NRNs should inquire about the lawyer’s track record in handling similar cases, their approach to litigation, and their availability to handle the matter effectively. Additionally, NRNs should clarify the fee structure and ensure there are no hidden costs associated with hiring the lawyer.
Selecting a litigation lawyer who understands their needs and is committed to achieving the best possible outcome is crucial for NRNs.
What documents are needed for court cases?
The documents needed for court cases in Nepal vary depending on the nature of the case. Generally, essential documents include any contracts, agreements, correspondence, evidence, and any other relevant paperwork related to the dispute.
For example, in a property dispute, documents such as land deeds, ownership certificates, and survey reports may be required. In a personal injury case, medical records, police reports, and witness statements is important.

How to file a lawsuit in Nepal as a NRN?

To file a lawsuit in Nepal, one must adhere to specific procedures outlined in the Civil Procedure Code and relevant laws. The process typically involves drafting a written complaint outlining the facts of the case, legal arguments, and the relief sought.
The complaint, along with any supporting documents, must be filed with the appropriate court having jurisdiction over the matter. Additionally, the plaintiff must pay the required court filing fees. Once the lawsuit is filed, the court will issue summons to the defendant, initiating the legal proceedings.
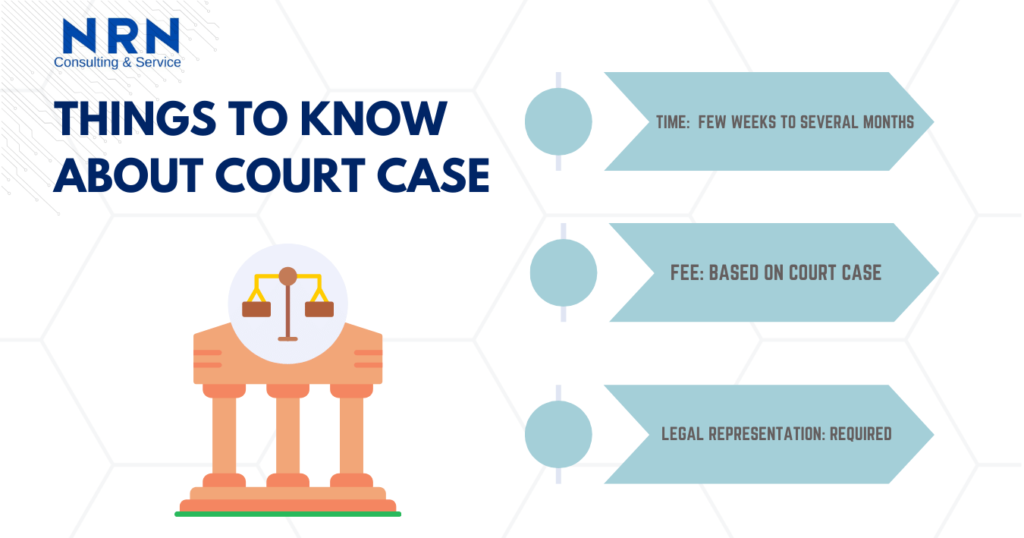
Are there court fees for NRNs?
Yes, there are court fees for NRNs filing lawsuits in Nepal. The court fees vary depending on the nature and value of the case, as well as the specific court where the lawsuit is filed. NRNs are required to pay these fees at the time of filing the lawsuit.
The fees cover various court expenses, including administrative costs and processing fees. It’s essential for NRNs to be aware of the applicable court fees and budget accordingly when initiating legal proceedings in Nepal. Additionally, consulting with a legal expert can provide clarity on the specific fees associated with their case.
Can NRNs represent themselves in court?
Yes, Non-Resident Nepalis (NRNs) have the right to represent themselves in court in Nepal. However, it’s important to consider the complexities of legal proceedings and the potential advantages of legal representation.
While NRNs can choose to act as their own legal representatives, doing so may present challenges, especially if they are unfamiliar with Nepali law and court procedures. Engaging a qualified lawyer can provide NRNs with legal guidance, expertise, and representation throughout the litigation process, increasing the likelihood of a favorable outcome.
How to handle court summons?
Handling court summons in Nepal requires prompt attention and compliance with the instructions provided. Upon receiving a court summons, individuals must carefully read the document to understand the nature of the legal proceedings, including the date, time, and location of the court appearance.
It’s crucial to adhere to the deadlines outlined in the summons and take appropriate action, whether it involves responding to the allegations, attending court hearings, or seeking legal advice. Ignoring or failing to respond to a court summons can have serious consequences, including default judgments or legal sanctions.
What are the court jurisdictions in Nepal?
In Nepal, courts are organized into various levels and jurisdictions, each with specific powers and responsibilities. The court system consists of District Courts, Appellate Courts, and the Supreme Court. District Courts have jurisdiction over civil, criminal, and administrative matters within their respective districts. Appellate Courts hear appeals from decisions made by District Courts and certain specialized courts.
The Supreme Court is the highest judicial authority in Nepal and has jurisdiction over constitutional matters, appellate jurisdiction over decisions of lower courts, and the power to interpret laws. Additionally, there are specialized courts such as the Special Court, which deals with cases related to corruption and other specified offenses.
Can NRNs appeal court decisions?
Yes, Non-Resident Nepalis (NRNs) have the right to appeal court decisions in Nepal. If dissatisfied with the outcome of a case, NRNs can file an appeal with the appropriate appellate court, seeking a review of the decision.
The appellate process typically involves submitting a written petition outlining the grounds for appeal and providing supporting evidence or legal arguments. The appellate court will then review the case, consider the arguments presented by both parties, and make a decision based on the merits of the appeal.
How long do court cases take?
The duration of court cases in Nepal varies depending on various factors such as the complexity of the case, the caseload of the court, and procedural requirements. Simple cases may be resolved relatively quickly, while complex cases involving multiple parties or intricate legal issues may take longer to conclude.
Additionally, delays can occur due to factors such as adjournments, evidence gathering, and procedural challenges. As a result, it is challenging to provide a precise timeframe for the resolution of court cases.
Are there specialized NRN court services?
While there may not be specialized court services exclusively dedicated to Non-Resident Nepalis (NRNs) in Nepal, NRNs can access legal services and representation like any other individual. NRNs can engage the services of qualified lawyers and law firms to handle their legal matters, including litigation, property disputes, business transactions, and other legal issues.
It’s essential for NRNs to select legal professionals with expertise in Nepali law and experience in handling cases involving NRNs. Some law firms may offer specialized services tailored to the needs of NRNs, such as assistance with property transactions, estate planning, and legal advice on matters affecting NRNs residing abroad.
How to prepare for a court hearing?
Preparing for a court hearing involves several key steps to ensure readiness and confidence in presenting one’s case effectively. First, thoroughly review all relevant documents and evidence pertaining to the case. Prepare a clear and concise outline of the key points to be addressed during the hearing.
Practice delivering testimony or arguments to enhance clarity and coherence. Dress appropriately and arrive punctually at the courthouse. Familiarize yourself with courtroom etiquette and procedures. Bring necessary documents, identification, and any supporting materials.
What are the rights of NRNs in court?
Non-Resident Nepalis (NRNs) have the right to fair and impartial treatment in court, regardless of their residency status. NRNs have the right to legal representation, the right to present evidence and arguments in their defense, and the right to appeal court decisions.
NRNs have the right to understand court proceedings and to have access to interpreters or translators if necessary.
How to access court records?
Depending on the court’s procedures, access to court records may be granted in person, by mail, or electronically. Some courts may have online portals or databases where individuals can search for and access court records remotely. However, access to certain sensitive or confidential information may be restricted to authorized personnel or parties involved in the case.
Can NRNs settle disputes out of court?
Yes, Non-Resident Nepalis (NRNs) can opt to settle disputes out of court through alternative dispute resolution (ADR) methods such as negotiation, mediation, or arbitration.
These methods offer a less adversarial and more collaborative approach to resolving conflicts, allowing parties to reach mutually acceptable agreements without the need for formal court proceedings.
NRNs may choose to engage in ADR to save time, costs, and maintain privacy, particularly in matters such as commercial disputes, family conflicts, or contractual disagreements.
What is the role of a notary in court?
In court, a notary serves as an impartial witness who verifies the authenticity of legal documents and certifies signatures. Notaries play a crucial role in ensuring the validity and legality of documents submitted as evidence or filed with the court.
Their responsibilities may include administering oaths, affirmations, or affidavits, as well as attesting to the identity of the signatories. Notaries help prevent fraud and misrepresentation by confirming that individuals signing documents do so willingly and with full understanding of their contents.
In court proceedings, notaries may be called upon to authenticate various types of documents, including contracts, deeds, wills, and powers of attorney.
How to handle legal notices?
Handling legal notices requires careful attention and prompt action to address the issues raised. Upon receiving a legal notice, individuals should carefully read and understand its contents, including the allegations, claims, or demands being made.
It’s crucial to adhere to any deadlines or instructions outlined in the notice, such as responding within a specified timeframe or appearing in court on a particular date. Ignoring or failing to respond to a legal notice can have serious consequences, including legal judgments entered against the recipient.
Individuals should consult with a qualified lawyer to assess the validity and implications of the notice and determine the appropriate course of action.
Can NRNs get court-appointed lawyers?
Court-appointed lawyers are typically provided for individuals who cannot afford legal representation and are facing criminal charges. However, court-appointed lawyers may not be available for civil cases or for Non-Resident Nepalis (NRNs) unless they meet specific criteria indicating financial need.
NRNs who require legal assistance but cannot afford private representation may explore options such as legal aid programs or pro bono services offered by law firms or non-profit organizations. NRNs may choose to engage a lawyer privately to represent their interests in court proceedings.
It’s essential for NRNs to inquire about available resources and consult with legal experts to determine the best course of action for obtaining legal representation.
How to enforce court judgments?
Enforcing court judgments in Nepal involves taking legal action to ensure that the terms of a court decision are carried out and upheld. Once a judgment is issued, the prevailing party may initiate enforcement proceedings to compel compliance by the losing party.
Enforcement methods may include seizure of assets, garnishment of wages, or other legal remedies to recover the awarded damages or compel performance of the court-ordered actions.
The enforcement process typically begins with filing an application with the court requesting enforcement and providing evidence of the judgment. The court will then issue orders directing the appropriate authorities to enforce the judgment.
Conclusion
NRN Services & Consulting is renowned for its leading lawyers in Nepal, including senior advocates and seasoned litigators with nationally acclaimed practices. The firm provides exceptional legal representation for Non-Resident Nepalis (NRNs) or can help find the right lawyer to meet their needs.
This article offers a comprehensive guide to handling legal matters in the courts of Nepal. NRNs have the right to file lawsuits in Nepal for various issues such as property disputes, business conflicts, and personal injury claims.
FAQs
Can NRNs file Court Case in Nepal?
Yes, Non-Resident Nepalis (NRNs) can file lawsuits in Nepal, following specific legal procedures. NRN Services & Consulting provides Legal Consultations for the appropriate legal remedy for NRN Court Cases.
What is the process for NRN Court Case in Nepal?
Step 1: Appropriate Legal Consultation
Step 2: Filing a Case in the Appropriate Court, Usually District Court
Step 3: Initiation of Legal Proceedings
Step 4: Advocacy, Witness and Evidence Examination
Step 5: Decision by the Court
How to hire a litigation lawyer?
Consider expertise, experience, and fees; schedule consultations with potential lawyers. Consult NRN Services & Consulting for NRN Legal Experts.
Are there court fees for NRNs?
Yes, NRNs must pay court fees based on the case's nature and value.
Can NRNs appeal court decisions?
Yes, NRNs can appeal decisions they find unsatisfactory to higher courts in Nepal.
